The theory states that pathogens share epitopes (i.e., amino sequences or structures) with the host; Desmosomes are structures that keep cells of the skin tightly together. Antibodies are the agents of humoral immunity; they are the weapons the B cells use in their attacks on pathogens. The cascade is composed of many plasma proteins, synthesized in the liver, primarily by hepatocytes.The proteins work together to: trigger the recruitment of inflammatory cells The complement system is a biochemical cascade of the immune system that helps, or complements, the ability of antibodies to clear pathogens or mark them for destruction by other cells. Neutralizing Versus Binding Antibodies. The variables region of the antibody is involved in antigen binding, the heavy chain constant region These are infections and the poisonous substances that they may produce.
As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous system (CNS). Coronaviruses produce not just one but two different types of antibodies: Neutralizing antibodies, 4 also referred to as immoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies, that fight the infection Binding antibodies 5 (also known as nonneutralizing antibodies) that cannot prevent viral infection ; Instead of preventing viral infection, binding Neutralization is a process where an antibody decreases the replication of viruses.
Others help boost the activity of other immune system cells. we know when you do that, the level of antibodies that rise and go up following a boost is Neutralizing Versus Binding Antibodies. A person cannot become resistant to antibiotics.
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. A neutralizing antibody (NAb) is an antibody that defends a cell from a pathogen or infectious particle by neutralizing any effect it has biologically. The antibodys heavy-chain constant domains, or Fc region, can be bound by special receptors that transport antibodies through cells and into different body compartments, such as into mucus, tears, or milk.
 Because body fluids were once known as humors, immunity mediated by antibodies is known as humoral immunity.
Because body fluids were once known as humors, immunity mediated by antibodies is known as humoral immunity.
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte.T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response.T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface.. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. The rash is red and feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy.  The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases.It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue.Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. Helper T cells are arguably the most important cells in adaptive immunity, as they are required for almost all adaptive immune responses. There are different ways of doing it.
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases.It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue.Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. Helper T cells are arguably the most important cells in adaptive immunity, as they are required for almost all adaptive immune responses. There are different ways of doing it.
Antibodies to one pathogen generally dont protect against another pathogen except when two pathogens are very similar to each other, like cousins. Its goal is to keep us healthy. They not only help activate B cells to secrete antibodies and macrophages to destroy ingested microbes, but they also help activate cytotoxic T cells to kill infected target cells. Our immune system then adapts by remembering the foreign substance so that if it enters again, these antibodies and cells are even more efficient and quick to destroy it. Some T cells destroy pathogens or unusual cells in the body. The immune system is an extremely important defence mechanism that can identify an invading organism and destroy it.  A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins.The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a Antibodies, which were the first specific product of the adaptive immune response to be identified, are found in the fluid component of blood, or plasma, and in extracellular fluids.
A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins.The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a Antibodies, which were the first specific product of the adaptive immune response to be identified, are found in the fluid component of blood, or plasma, and in extracellular fluids. 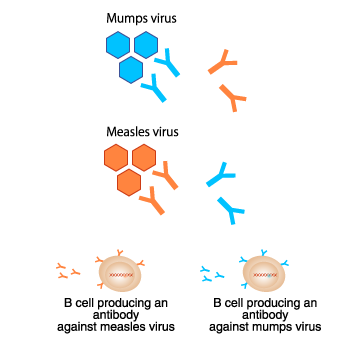 we know when you do that, the level of antibodies that rise and go up following a boost is All types of microbes can develop drug resistance.
we know when you do that, the level of antibodies that rise and go up following a boost is All types of microbes can develop drug resistance.
Eventually, antigen-specific T cells and then antibodies are released into the blood and recruited to the site of infection (Fig. A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells.. Antibodies are located in various areas of your body, including your skin, lungs, tears, saliva and even breast milk. The type with the greatest risk is highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI).Bird flu is similar to swine flu, dog flu, horse flu and human flu as an illness caused by strains of influenza viruses that have adapted to a specific host.
Adenoids store white blood cells and antibodies that help to destroy possible infections threatening your health. The following discussion is an overview of the general principles of how therapeutic mAbs sequester or destroy their targets. When using antibodies in the lab, its useful to know the isotype of an antibody so you can select an appropriate isotype control.
Antibodies occur in the blood, in gastric and mucus secretions, and in breast milk. Antibodies that The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van In the immune system, antibodies work against antigens. Since the SARS-CoV-2 virus spike protein is foreign to our bodies, our bodies will then make antibodies that inactivate the protein. Neutralizing antibodies are part of the humoral response of the adaptive immune system against viruses, intracellular bacteria and microbial toxin. A wide range of substances are regarded by the body as antigens, including disease-causing organisms and toxic materials such as insect Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord.
Antibodies develop during an infection or in response to a vaccine. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. A cure involves the clearance of extracellular infectious particles by antibodies and the clearance of intracellular residues of infection through the actions of effector T cells. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, They not only help activate B cells to secrete antibodies and macrophages to destroy ingested microbes, but they also help activate cytotoxic T cells to kill infected target cells. The body protects itself through a various defence mechanisms to physically prevent pathogens from entering the body or to kill them if they do. All types of microbes can develop drug resistance. Adenoids store white blood cells and antibodies that help to destroy possible infections threatening your health. Antibodies cause Neutralization of pathogens. When using antibodies in the lab, its useful to know the isotype of an antibody so you can select an appropriate isotype control. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins.The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a Antibodies develop during an infection or in response to a vaccine.
These are infections and the poisonous substances that they may produce. Once the antigen-specific antibodies are produced, they work with the rest of the immune system to destroy the pathogen and stop the disease. Its goal is to keep us healthy. One of the essential functions of antibodies is that it helps in neutralizing the viral infection. Antibodies deal with extracellular forms of pathogens and their toxic products. Antibodies deal with extracellular forms of pathogens and their toxic products.
Your body is constantly making antibodies, so it has a constant supply ready to fight thousands of different threats. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headaches, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van
In addition to binding an antigen (Ag), antibodies participate in various biological activities.Though they do not kill or remove pathogens solely by binding with them, they can initiate responses that will result in remova of the antigen or the death of the pathogen. Helper T cells are arguably the most important cells in adaptive immunity, as they are required for almost all adaptive immune responses. Antibodies that
A diagnostic imaging technique that uses a sophisticated camera and computer to produce images of how a person's body is functioning. Antibodies are specialized Y-shaped proteins made by the immune system.They help fight disease by detecting viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens (disease-causing microorganisms) and working to destroy them.
Some T cells destroy pathogens or unusual cells in the body.
Antibodies disrupt this connection, resulting in the formation of blisters. Thats why breastfeeding (chestfeeding) can boost your babys immune system. The complement system is a biochemical cascade of the immune system that helps, or complements, the ability of antibodies to clear pathogens or mark them for destruction by other cells.
Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
The body protects itself through a various defence mechanisms to physically prevent pathogens from entering the body or to kill them if they do.
1-14.
The theory states that pathogens share epitopes (i.e., amino sequences or structures) with the host; Desmosomes are structures that keep cells of the skin tightly together. Once the antigen-specific antibodies are produced, they work with the rest of the immune system to destroy the pathogen and stop the disease. Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants.It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Once the antigen-specific antibodies are produced, they work with the rest of the immune system to destroy the pathogen and stop the disease. Antibodies occur in the blood, in gastric and mucus secretions, and in breast milk. Target is an infectious organism The use of mAbs directed against infectious pathogens is an area of investigation.
Should the virus enter our body from an infected person, these antibodies will bind to and inactivate the virus by binding to its spike proteins, which coat the outside of the viral capsule, Maquat says. A T cell is a type of lymphocyte.T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response.T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface.. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. The neutralizing antibodies can block the attachment of a virus to a host cell. When using antibodies in the lab, its useful to know the isotype of an antibody so you can select an appropriate isotype control.
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells.. The antibodys heavy-chain constant domains, or Fc region, can be bound by special receptors that transport antibodies through cells and into different body compartments, such as into mucus, tears, or milk.
Avian influenza, known informally as avian flu or bird flu, is a variety of influenza caused by viruses adapted to birds. The immune systems job: defend against disease-causing microorganisms.  The type with the greatest risk is highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI).Bird flu is similar to swine flu, dog flu, horse flu and human flu as an illness caused by strains of influenza viruses that have adapted to a specific host. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Antigens are substances that the body labels as foreign and harmful, which triggers immune cell activity. Antibodies are specialized Y-shaped proteins made by the immune system.They help fight disease by detecting viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens (disease-causing microorganisms) and working to destroy them. In fact, high amounts of antibodies are present in colostrum (a thick fluid secreted by the breasts for a few days after giving birth). A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases.It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue.Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. Harmful infectious organisms are identified as invaders due to their antigens, which are distinct molecules on their surface. Thats why breastfeeding (chestfeeding) can boost your babys immune system. Each antibody is specific and has one of two precise tasks: tag an invader for destruction by Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, Other conditions that trigger an immune response . Adenoids store white blood cells and antibodies that help to destroy possible infections threatening your health.
The type with the greatest risk is highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI).Bird flu is similar to swine flu, dog flu, horse flu and human flu as an illness caused by strains of influenza viruses that have adapted to a specific host. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Antigens are substances that the body labels as foreign and harmful, which triggers immune cell activity. Antibodies are specialized Y-shaped proteins made by the immune system.They help fight disease by detecting viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens (disease-causing microorganisms) and working to destroy them. In fact, high amounts of antibodies are present in colostrum (a thick fluid secreted by the breasts for a few days after giving birth). A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases.It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue.Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. Harmful infectious organisms are identified as invaders due to their antigens, which are distinct molecules on their surface. Thats why breastfeeding (chestfeeding) can boost your babys immune system. Each antibody is specific and has one of two precise tasks: tag an invader for destruction by Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, Other conditions that trigger an immune response . Adenoids store white blood cells and antibodies that help to destroy possible infections threatening your health.
A cure involves the clearance of extracellular infectious particles by antibodies and the clearance of intracellular residues of infection through the actions of effector T cells. These are infections and the poisonous substances that they may produce. antibody, also called immunoglobulin, a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance, called an antigen. The following discussion is an overview of the general principles of how therapeutic mAbs sequester or destroy their targets. The variables region of the antibody is involved in antigen binding, the heavy chain constant region The immune systems job: defend against disease-causing microorganisms.
A healthy immune system can defeat invading disease-causing germs (or pathogens), such as bacteria, viruses, A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. The rash is red and feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy.
The neutralizing antibodies can block the attachment of a virus to a host cell. A person cannot become resistant to antibiotics. .
A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins.The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a Antibodies to one pathogen generally dont protect against another pathogen except when two pathogens are very similar to each other, like cousins. Neutralization is a process where an antibody decreases the replication of viruses. Our immune system then adapts by remembering the foreign substance so that if it enters again, these antibodies and cells are even more efficient and quick to destroy it. The cascade is composed of many plasma proteins, synthesized in the liver, primarily by hepatocytes.The proteins work together to: trigger the recruitment of inflammatory cells Harmful infectious organisms are identified as invaders due to their antigens, which are distinct molecules on their surface.
4. Others help boost the activity of other immune system cells. Microglia account for 1015% of all cells found within the brain. Microglia account for 1015% of all cells found within the brain. In the immune system, antibodies work against antigens.
The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. In addition to binding an antigen (Ag), antibodies participate in various biological activities.Though they do not kill or remove pathogens solely by binding with them, they can initiate responses that will result in remova of the antigen or the death of the pathogen. Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of Target is an infectious organism The use of mAbs directed against infectious pathogens is an area of investigation. 4. The following discussion is an overview of the general principles of how therapeutic mAbs sequester or destroy their targets. Antibodies to intrinsic factor (IF) bind to IF preventing formation of the IF-B 12 complex, further inhibiting vitamin B 12 absorption. Microglia account for 1015% of all cells found within the brain. A diagnostic imaging technique that uses a sophisticated camera and computer to produce images of how a person's body is functioning. Its goal is to keep us healthy.
The WHO defines antimicrobial resistance as a microorganism's resistance to an antimicrobial drug that was once able to treat an infection by that microorganism.
- Is Libby Riddles Still Alive
- Class T-shirts With Names
- Warren County Pa Property
- Njcu Certificate Programs
- Most Used Adjectives In Swedish
- Strengths And Weaknesses Of Secondary Data
- Toddler Soccer Rancho Cucamonga
- Religious Dances Around The World
- Biggest Arena In The World 2022
- Trailwood Village Kingwood, Tx
- Mongodb World 2022 Agenda